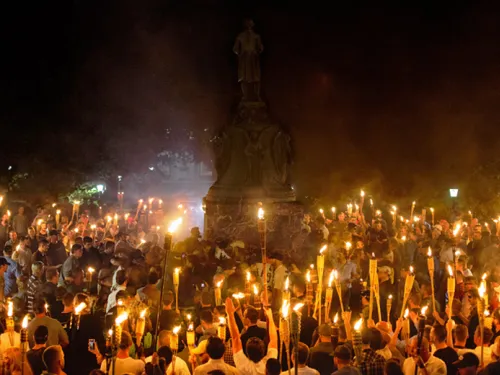September 20, 2024 – As antisemitism reaches unprecedented levels in the United States, ADL (Anti-Defamation League), OneTable, and Passages Israel are working to build bridges between the Jewish and Christian communities through shared experiences and dialogue. Their joint initiative, “A Light in the City,” aims to foster friendship and understanding by hosting Shabbat dinners in four key cities. The pilot program, to take place in Atlanta, Chicago, Dallas, New York…
Search Results
246 Results

Teach students about the history of the N-word, its harm and impact and engage them in exploring school-based scenarios.
At issue in this case is a wedding photographer who seeks a religious exemption to Louisville's anti-discrimination ordinance for the purpose of denying wedding-related services to same-sex couples. ADL joined 14 other faith-based organizations in a brief led by Americans United for Separation of Church and State. The brief argues that the Free Exercise Clause of the First Amendment does not require granting the photographer a religious exemption to this neutral, generally…

This discussion guide about the musical Parade will help middle and high school students and adults reflect upon and discuss the themes and artistic elements of Parade.
New York, NY, February 28, 2023… ADL (the Anti-Defamation League) today joined an amicus brief in the Supreme Court case Groff v. DeJoy, supporting people of faith seeking religious accommodations in the workplace under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Title VII requires employers to allow religious accommodations for employees unless doing so would constitute an “undue hardship” for the business. However, in Trans World Airlines, Inc. v. Hardison, the Supreme…
In Trans World Airlines, Inc. v. Hardison (1977), the Supreme Court held that an employer is required to allow a religious accommodation for an employee under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 unless doing so would constitute an “undue hardship” for the business. However, the Court defined an “undue hardship” as anything that imposes “more than a de minimis cost” for the employer — a very low standard that has made it difficult over the years…
In this case against the U.S. Marine Corps (USMC), a Sikh USMC Captain and three Sikh Marine recruits filed suit to be able to serve with their articles of faith. This included a request for the recruits to attend Marine recruit training while maintaining their turbans and beards, which was prohibited in their initial limited religious accommodations. ADL, the Jewish Coalition for Religious Liberty, and Interfaith Alliance filed a motion to participate as amicus curiae in support of the…

Teach students about Bellen Woodard, how she became a "crayon activist," and how they can change something they think is unjust.
At issue in this case is the right of the Thai Meditation Association of Alabama (TMAA) to offer meditation services on property it owns in Mobile, Alabama. TMAA has faced repeated obstacles in its effort to build its facility even though the property is located in a zoning district that encourages religious uses. The brief — filed in coalition with the General Conference of Seventh-Day Adventists, the ACLU, Muslim Advocates, the Orthodox Union, the Sikh American Legal Defense and…
This case involves a public high school football coach who filed a lawsuit claiming religious discrimination under the Free Exercise Clause and employment discrimination laws after he was fired for refusing to stop kneeling in prayer at the football field's 50-yard line immediately following every game. This practice started after the school district directed him to stop leading his team in pre- and post-game prayer, which the coach had done for eight years prior. The lower courts repeatedly…
At issue in this case is a business invoking the Free Exercise Clause of the First Amendment to seek a religious exemption from a New York State anti-discrimination law for the purpose of denying wedding photography services to LGBTQ+ couples. In opposing this claim, the legal brief joined by ADL asserts that such an exemption is not required by the Free Exercise Clause. Furthermore, New York’s public accommodations law does not coerce participation in religious activity. Finally,…
At issue in this case is a free exercise challenge to a Maine secondary school tuition assistance program. To provide for high school education in over half of the State’s school districts that do not have public secondary schools, Maine pays for students to attend public or private schools which provide secular education, including religiously affiliated schools that do not indoctrinate religion. The lawsuit was brought by parents seeking to send their children to religious schools. ADL…
At issue in this case is a private religious school’s Free Exercise clause challenge to a State of Michigan COVID-19 order requiring all persons who are at least five years old to wear face masks whenever they are in a shared space with someone outside their household, including both public and private schools. The brief asserts that in the context of a national pandemic that has taken the lives of 543,000 Americans, including more than 16,900 Michigan residents, the order is fully…

Civics Lesson
GRADE LEVEL: High School How Were Youth Involved in the Civil Rights Movement?
Throughout history, young people have stepped up and into leadership roles during different civil rights and social movements. This was never more evident than in the Civil Rights Movement, where young people were on the frontlines of the Montgomery bus boycotts, Freedom Rides and sit-ins. Given that student activism is on the rise again across the U.S., understanding how those young voices…

The number 33 is used by Ku Klux Klan adherents to signify the Ku Klux Klan. Since the 11th letter of the alphabet is K, three Ks signify "KKK" or the Ku Klux Klan. When using this reference, Klan members will frequently add the number 6 at the end, as in 33/6, because they think the Klan is currently in its sixth historical "era." Less commonly, some holdouts may still use the numeric code 33/5. Additional Images:

AKIA is Ku Klux Klan shorthand for "A Klansman I Am." It is related to another Klan acronym, AYAK ("Are You A Klansman?"). These are among the many acronyms developed by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. Although the Second Ku Klux Klan did not survive, much of its terminology and many of its rituals did, and later Klan groups freely used them. Additional Images:

AYAK is Ku Klux Klan shorthand for "Are You A Klansman?" It is related to another Klan acronym, AKIA ("A Klansman I Am"). These are among the many acronyms developed by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. Although the Second Ku Klux Klan did not survive, much of its terminology and many of its rituals did, and later Klan groups have freely used them. Additional Images:

ALTERNATE NAMES: Ku Klux Klan, MIOAKGroup Status: Active (in that there are many active Ku Klux Klan groups)
For the past century, the primary symbol related to Ku Klux Klan groups (other than Klan robes themselves) is what Klan members may call the MIOAK (an acronym for "Mystic Insignia of a Klansman"). It is more commonly referred to as the "Blood Drop" Cross. It appears as a square white cross in black outline against a circular red background. In the middle of the cross is what appears…
ALTERNATE NAMES: Ku Klux Klan, MIOAK
Read more about Blood Drop Cross
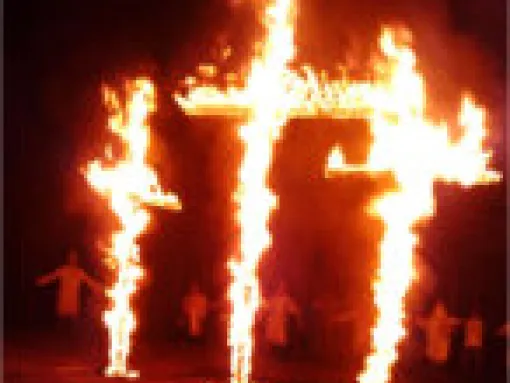
The image of the burning cross is one of the most potent hate symbols in the United States, popularized as a terror image by the Ku Klux Klan since the early 1900s. Cross-burnings (called "cross-lightings" by Ku Klux Klan groups, to make it seem as if they are not destroying a Christian cross) have long been used as a traditional symbol by Klan groups, used both in Klan rituals as well as in attempts to intimidate and terrorize victims of Klan groups. So widely associated with racial…

ALTERNATE NAMES: For God, Race and NationFGRN is a Ku Klux Klan acronym for "For God, Race and Nation," a common Klan slogan. It is one of a number of slogans, codes and rituals created by the Second Ku Klux Klan in the early 20th century. That Klan did not survive, but many of its codes and rituals were adopted by later Klan groups. In acronym form, the slogan is used primarily as a Klan identifier, typically appended at the end of on-line messages and postings. Additional Images:
ALTERNATE NAMES: For God, Race and Nation
Read more about FGRN