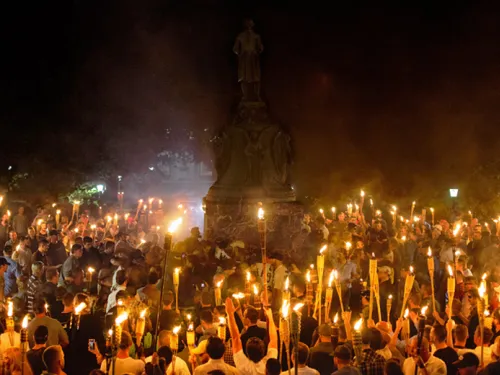The Orange County, Florida Human Rights Ordinance provides broader anti-discrimination protections than the State’s Human Rights Law, including prohibitions on sexual orientation and gender identity discrimination. At issue in this case is whether the State law preempts these broader protections. ADL joined a brief asserting that the Florida Constitution and long-standing State Supreme Court rulings permit county and municipal governments to adopt more comprehensive anti…
Search Results
89 Results
Mississippi passed a law in 2018 that bars abortions after the 15th week of pregnancy, with limited exceptions. ADL joined with the National Women’s Law Center and 71 other organizations on an amicus brief urging that the law — an unmistakable challenge to Roe v. Wade — be found unconstitutional. The brief focuses on due process and explains that the devastating impact of allowing a pre-viability abortion ban to stand — or overturning the right to abortion entirely …
At issue in this case is the application of the First Amendment’s ministerial employee exception to an art teacher at a religious elementary school. Grounded in constitutionally mandated separation of church and state, the exception exempts religious institutions from all employment discrimination laws for employees deemed to be ministerial. A lower state court ruled that the teacher, who performed no “vital religious duties,” could move forward with her pregnancy and marital…
Alabama only allows people to change the gender marker on their driver’s licenses if they undergo surgical procedures and submit proof to the state, meaning that transgender people who do not want, cannot afford, or are medically unable to have the required surgeries are prevented from having a license that accurately reflects their gender. Carrying a license with an inaccurate gender marker puts transgender people — especially Black and brown transgender women — at a…
In March 2019, the United States Senior Women's National Soccer Team (USWNT) filed a class action lawsuit against the United States Soccer Federation, Inc. (USSF), claiming violations of the Equal Pay Act and of Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 alleging unequal pay and working conditions as compared to the Men’s National Team (USMNT) in the District Court of Central California. For years, the U.S. Soccer Federation had been paying USWNT players less than their counterparts on…

The phrase “You Will Not Replace Us” is a white supremacist slogan referring to the common White supremacist belief that the white race is in danger of going extinct due to rising numbers of non-White people who are controlled and manipulated by Jews. It may also be seen in acronym form as YWNRU.
ALTERNATE NAMES: YWNRU, Jews Will Not Replace Us

GTKRWN is an acronym for a racist and antisemitic slogan created by white supremacists: “Gas the Kikes; Race War Now.”
ALTERNATE NAMES: GTK
Read more about GTKRWN
This case involves a legal challenge to Massachusetts’s anti-bullying statute — namely, that the “emotional harm” prong of the definition of bullying in M.G.L. c. 71, section 37O(a) is unconstitutionally overbroad and vague. ADL has been a key proponent of anti-bullying legislation in Massachusetts and accordingly joined an amicus brief, prepared by GLBTQ Legal Advocates & Defenders (GLAD), to emphasize the vital importance of the emotional harm prong of the…
Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 prohibits voting practices and procedures that discriminate on the basis of race, color, or membership in language minority groups. In this case, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit held that two Arizona election provisions — one that prohibits third-party ballot collection and another that prohibits the counting of out-of-precinct votes — violated Section 2 because of their discriminatory impact on communities of color. The…
At issue in this case is the extent to which K-12 schools can regulate student speech that occurs off-campus. ADL joined a brief prepared by the National Women’s Law Center, Lambda Legal Defense and Education Fund and Lawyers’ Committee for Civil Rights Under Law, urging the Court to ensure that when it comes to off-campus speech, schools can regulate student bullying, harassment, or threats, but not speech that is merely perceived to substantially disrupt school activities. The…

ACAB stands for "All Cops Are Bastards" and is a slogan of long standing in the skinhead subculture. Because non-racist skinheads may use this acronym as well as racist skinheads, it should be carefully judged in the context in which it appears.

AKIA is Ku Klux Klan shorthand for "A Klansman I Am." It is related to another Klan acronym, AYAK ("Are You A Klansman?"). These are among the many acronyms developed by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. Although the Second Ku Klux Klan did not survive, much of its terminology and many of its rituals did, and later Klan groups freely used them. Additional Images:

AYAK is Ku Klux Klan shorthand for "Are You A Klansman?" It is related to another Klan acronym, AKIA ("A Klansman I Am"). These are among the many acronyms developed by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. Although the Second Ku Klux Klan did not survive, much of its terminology and many of its rituals did, and later Klan groups have freely used them. Additional Images:

ALTERNATE NAMES: For God, Race and NationFGRN is a Ku Klux Klan acronym for "For God, Race and Nation," a common Klan slogan. It is one of a number of slogans, codes and rituals created by the Second Ku Klux Klan in the early 20th century. That Klan did not survive, but many of its codes and rituals were adopted by later Klan groups. In acronym form, the slogan is used primarily as a Klan identifier, typically appended at the end of on-line messages and postings. Additional Images:
ALTERNATE NAMES: For God, Race and Nation
Read more about FGRN

HFFH is an acronym used by the Hammerskins, a large racist skinhead gang. It stands for "Hammerskins Forever, Forever Hammerskins," a format probably adopted from biker gangs. Additional Images:

Group Status: Active
HSN is an acronym used by the Hammerskins, a large racist skinhead gang. It stands for "Hammerskin Nation," which is a collective reference to the various regional Hammerskin gangs such as the Confederate Hammerskins, Western Hammerskins, etc. Additional Images:

ITSUB is a Ku Klux Klan acronym for "In The Sacred Unfailing Being," a reference to God. It is one of many Klan acronyms created by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. That Klan did not survive, but subsequent Ku Klux Klan groups continued many of its rituals and codes. Today, ITSUB has no real meaning or particular purpose and is typically used by Klan group members in on-line messages or posts solely as a way to identify themselves with the Ku Klux Klan. This has been the fate of a…

KABARK is a Ku Klux Klan acronym for "Konstantly Applied By All Regular Klansmen." It is one of many acronyms and codes developed by the Second Ku Klux Klan in the early 20th century. The Second Ku Klux Klan did not survive, but later Klan groups continued many of its codes and rituals. Today, KABARK is essentially meaningless and only used as a "sign off" in on-line messages by Klan group members, along with several other similar archaic acronyms. Additional Images:

KIGY is Ku Klux Klan shorthand for "Klansman I Greet You." It is one of many acronyms developed by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. Although the Second Ku Klux Klan did not survive, much of its terminology and many of its rituals did, and later Klan groups freely used them. Additional Images:

KLASP is a Ku Klux Klan acronym for "Klannish Loyalty, A Sacred Principle." It is one of many Klan acronyms created by the Second Ku Klux Klan that emerged in 1915. That Klan did not survive, but subsequent Ku Klux Klan groups continued many of its rituals and codes. Today, KLASP has no real meaning or particular purpose and is typically used by Klan group members in on-line messages or posts solely as a way to identify themselves with the Ku Klux Klan. This has been the fate of a number of…